Everything You Need To Know About Inverted Arch Footing

What is Inverted Arch Footing in Construction?
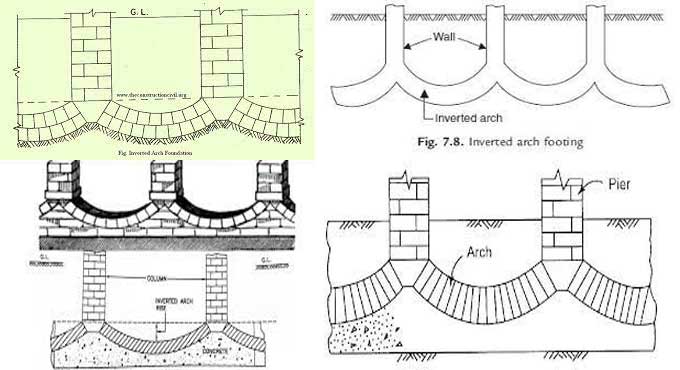
Inverted arch footings, also known as arch-shaped footings or inverted T-shaped footings, are structural elements used in construction to support loads from columns or walls. They are designed to distribute the load over a larger area, reducing the pressure on the soil and preventing excessive settlement.
The name inverted arch comes from the shape of the footing, which resembles an arch that is turned upside down. The inverted arch footing consists of a horizontal slab or beam that spans between two or more vertical columns or walls, forming an arch-shaped structure beneath the ground surface.
These footings are commonly used in situations where the soil has poor bearing capacity or when there is a need to minimize settlement. By distributing the load over a wider area, the pressure on the soil is reduced, thereby preventing excessive settlement and maintaining the stability of the structure.
Other Factors
The inverted arch footing transfers the load from the columns or walls to the soil through the arch-shaped structure. The shape of the arch helps in redirecting the applied load to the sides of the footing, which in turn transfers the load to the surrounding soil. This mechanism allows for better load distribution and minimizes the risk of differential settlement.
Inverted arch footings are often used in foundation systems for structures such as bridges, retaining walls, and tall buildings. The design of these footings requires careful consideration of factors such as the soil conditions, the magnitude and distribution of the loads, and the overall stability requirements of the structure.
It is important to note that the design and construction of inverted arch footings should be carried out by qualified structural engineers who take into account the specific requirements and conditions of the project.
Why are Inverted Arch Footings used in Construction?
Inverted arch footings, also known as arch foundations, are used in construction for several reasons:
1. Load distribution: Inverted arch footings are effective in distributing heavy loads, such as those from columns or walls, over a larger area. The arch shape helps to evenly distribute the load to the surrounding soil or bedrock, reducing the stress on the foundation and minimizing the risk of settlement or structural failure.
2. Soil improvement: In cases where the soil has poor bearing capacity or is prone to settlement, inverted arch footings can be used to improve the stability of the foundation. The arch shape creates a larger contact area with the soil, distributing the load more effectively and reducing the pressure on the underlying soil layers.
3. Bridge construction: Inverted arch footings are commonly used in bridge construction, particularly for piers and abutments. They provide a stable foundation for supporting the vertical loads from the bridge structure and also help to counteract the lateral forces exerted by the bridge, such as wind or seismic loads.
4. Structural efficiency: The arch shape of inverted arch footings allows for efficient use of materials, as it can resist compressive forces more effectively than a flat slab foundation. This can result in cost savings and improved structural performance.
5. Aesthetics: In some cases, inverted arch footings are used for architectural or aesthetic purposes. They can add visual interest to a building or structure, especially when exposed or incorporated into the design.
Inverted arch footings are suitable for different projects based on their specific requirements, site conditions, and engineering considerations. In order to determine the most suitable foundation type for a construction project, soil conditions, structural design, and load requirements must be thoroughly examined.
What are the advantages of using Inverted Arch Footings in Construction?
Here are some of the benefits associated with using inverted arch footings:
1. Load distribution: Inverted arch footings are designed to distribute the load from the structure over a larger area. The arch shape allows for a wider distribution of the load, reducing the stress on the soil and preventing excessive settlement. This load distribution capability makes inverted arch footings particularly suitable for structures with heavy loads or on weak soil conditions.
2. Increased bearing capacity: By enlarging the base of the foundation, inverted arch footings can significantly increase the bearing capacity of the soil. The under-reamed piles create a larger contact area with the soil, effectively improving the load-bearing capacity of the foundation system. This enables the construction of structures in areas with weaker soils or where deep foundations would be required.
3. Stability and settlement control: Inverted arch footings enhance the stability of the structure by providing a wider support base. The arch shape helps to resist lateral forces and reduces the likelihood of differential settlement. This is especially beneficial in areas with variable soil conditions or where differential settlement could lead to structural damage.
4. Cost-effectiveness: In some cases, inverted arch footings can be a cost-effective alternative to other foundation systems. By utilizing the existing soil and improving its load-bearing capacity, the need for extensive excavation, deep foundations, or costly ground improvement techniques may be reduced. This can result in cost savings during the construction process.
5. Time-efficient installation: Inverted arch footings can be relatively quick to install compared to other deep foundation systems. The under-reaming process, which involves enlarging the bottom of the pile, can be carried out using specialized equipment, allowing for efficient and rapid installation. This can help in accelerating the construction schedule and reducing overall project duration.
What are the disadvantages of using Inverted Arch Footings in construction?
While they have some advantages, there are also a few potential disadvantages associated with their use. Here are some of the drawbacks:
1. Increased complexity and cost: Inverted arch footings require additional materials and construction techniques compared to traditional footings. The complexity of their design and construction can lead to higher costs, including labor, materials, and engineering expertise.
To learn more, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: Smart Engineer
2. Limited suitability for certain soil conditions: The effectiveness of inverted arch footings depends on the soil conditions at the construction site. They are typically used in situations where the soil has poor load-bearing capacity or when there is a need to distribute the load over a larger area. However, in soils with high water tables or expansive clay, the design may not be suitable, as it can lead to uneven settlement or differential movement.
3. Increased construction time: The construction process for inverted arch footings is more time-consuming compared to standard footings. The additional steps involved, such as formwork installation and concrete pouring, can prolong the construction schedule.
4. Maintenance challenges: The inverted arch design can present challenges when it comes to maintenance and repair. If any issues arise with the footing, such as cracks or settling, it may be more difficult and costly to rectify due to the complexity of the design.
5. Limited flexibility in design modifications: Inverted arch footings are relatively inflexible once constructed. Making modifications or adjustments to the foundation design in the future can be challenging, requiring extensive structural changes or even demolition and reconstruction.