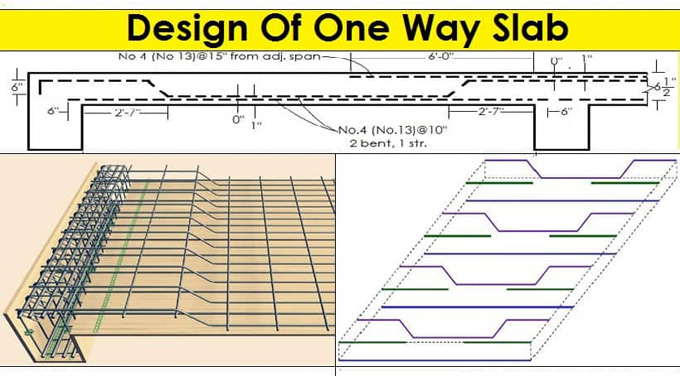
Steps for Designing a One-Way Slab

The one-way slab acts as the foundation of the building structure. In the case where the ratio of the longer span to the shorter span is greater than 2, the slabs of the construction structure are supported on all four corners, and thus, it acts as a one-way slab. The one-way slab bends and spans only in one direction.

Discuss the different types of one-way slabs used in the construction site
The one-way slab has been available in different types, which are as follows:
One-way solid slab with beams
In these types of one-way slab, the beams are used to support the slab. This one-way solid slab system has been created to resist different types of load conditions on the basis of the arrangement of beams and columns.
One-way ribbed slab
The one-way ribbed slab has been used in low-rise office buildings, warehouses or parking garages.
One-way ribbed slab with integral beams
The one-way ribbed slab, along with internal beams, has a broader span than the one-way solid slabs. The installation process of the one-way ribbed skab, along with the internal beam, is cost-effective as it has been used as a modular or prefabricated structure.
Applications of the one-way slab in the construction project
The one-way slab has been designed to carry loads of the building structure in one direction, which is important to select the appropriate structural system for the different types of building structures. Due to this, the one-way slab has been installed in different types of construction work.
1. The one-way slab has been used in single-storey buildings and low-rise apartments, as it is ideal for the roof and floors, along with a shorter span.
2. In the case of the small commercial buildings, along with a straightforward layout, the installation of the one-way slab acts as an economical flooring solution.
3. In the case of the warehouse or factories, in which uniform loads are required and have shorter spans, the one-way slab can be installed and offers cost-effectiveness and simplicity.
Load factors influencing the one-way slab design process
Dead loads
The assessment of the dead loads on the one-way slabs should be determined, as the dead loads can form the baseline for the other types of loads. In the case of underestimating the dead loads, there can be insufficient structural support for the slabs.
Dynamic loads
The dynamic loads can induce additional stress and deflection on the one-way slabs, so it is necessary to carefully analyse the dynamic loads of the one-way slabs.
Live loads
The live load on the one-way slab should also be analysed to ensure the structural integrity of the one-way slab.
Requirements for designing a one-way slab
The appropriate bar size
The size of the bars that have been used in the one-way slab should be selected accurately, so that the actual distance is not less than 1.5 times the thickness of the slab. This feature helps to avoid paying too much for the handling and fabrication of the bars.
Comprehensive strength
The comprehensive strength of the concrete used in the one-way slab should be determined on the basis of the requirements of the building structures for long-term durability. Due to the durability requirements of the slabs, concrete with high compressive strength should be used.
A certain distance between steel bars
The maximum space between the bars should not be more than three times the thickness of the slab. The maximum thickness among the reinforcement bars should be five times the thickness of the slabs.
Learn about the design procedure of the one-way slab
The design process of the one-way slab involves several steps, which are as follows:
1. At first, the span loads in the one-way slab should be determined at the beginning of the design process.
2. In the next step of the design procedure, the builder has to determine the design movement and the shear moment by using the simplified methods.
3. In the next step, the flexural reinforcement should be estimated. In this context, the builders have to check the area of reinforcement against the maximum and minimum requirements. The number of bars within the one-way slab is also determined at this stage.
4. After that, the temperature reinforcement has been provided perpendicularly to the main steel, which helps to prevent cracking of the slabs from the thermal expansion and contraction process.
To learn more, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: AF Math & Engineering
5. In the next step, the design of the one-way slab should be verified for shear, which helps to ensure that the one-way slab can resist the shear forces.
6. In the final step, the builders have to ensure that bars have been placed based on the maximum and minimum spacing requirements of the relevant codes. In addition, the development length requirement should also be checked for the reinforcement.