Shallow Foundation and its types

The shallow foundation is categorized as follow :-
1. Spread Footing
2. Combined Footing
3. Raft Foundation
4. Annular Slab or Ring Foundation.
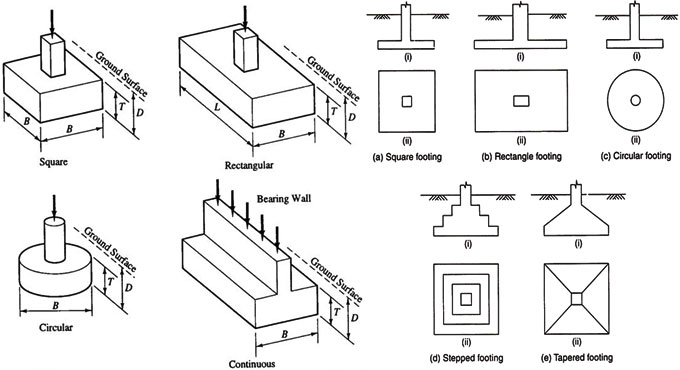
Type 1. Spread Footing: Foundation that transmits the load from a wall or column to a deeper width is called spread foundation or footing. The spread footing intended to the walls of a load bearing structure is called wall footing, continuous footing, or strip footing.
i. Strip Footings: Strip footing is made of stone masonry or concrete and it contains a stepped cross section. Now-a-days, the concrete is gaining popularity in construction industries and the load bearing structures & strip footings become outdated to some extent exclusive of small lightly loaded residential buildings. It is also called continuous footing or wall footing.
ii. Isolated Footing: Spread footing arranged to the columns of a framed structure is known as isolated footing, column footing, or pad foundation.
It is arranged underneath the column to disperse the loads securely to the bed soil. This type of footing is provided to support single-columns and when the columns are placed comparably at long span. It is very cost-effective.
Type 2. Combined Footing: Combined footing is effective when footings of two adjoining columns are provided too narrowly or overlap. It is categorized as follow :-
i. Rectangular Footing: Combined footing is usually rectangular in shape to resist equivalent column loads.
ii. Trapezoidal Footing: For irregular column loads, trapezoidal footing should be utilized to make sure that the centre of gravity (CG) of the column loads overlaps with the CG of the foundation in plan.
iii. Strap Footing: For footings located adjacent to the property lines, a strap footing should be applied to make sure that the edge of the footing adjacent to property line is not expanded into the nearby site. Under the situation, the footing adjacent to the property line (exterior footing) is attached with the footing inside the site (interior footing) via a strap beam.
The strap beam transmits the load of the exterior column footing merely to the interior footing during structural action.
Type 3. Raft Foundation: Raft foundations also known as raft footings or mat foundations, are provided with reinforced concrete slabs having consistent thickness (normally 150 mm to 300 mm) which are extended for a wide area, often the entire footprint of a building. They disperse the load enforced through a number of columns or walls over the area of foundation.
Raft foundation is mainly arranged when the entire area of all footings surpasses 50% of the loaded area. It is also suitable for heavy structures situated over highly compressible and weak soils expanding to large depth.
Type 4. Annular Slab or Ring Foundation: A ring foundation is sometimes arranged for a bigger water tank with its columns attached through a ring beam and supported across an annular slab.